Degenerate Gases on Atom Chips
Degenerate Gases on Atom Chips
Members
- Permanent staff : Isabelle Bouchoule
- PhD student : Guillaume Themèze
- Former PhD students : Léa Dubois, Maximilian Schemmer, Aisling Johnson, Bess Fang, Tarik Berrada as part time (co-tutelle with atom-chip group of Atomic Institute - Vienna University), Thibaut Jacqmin, Julien Armijo, Jean-Baptiste Trebbia, Jérôme Estève, Thorsten Schumm, Christine Aussibal
- Former Post-doc : Carlos Garrido-Alzar
!!! Students welcome !!!
Introduction
|
|
We study the physics of one-dimensional Bose gases using an atom chip set-up. Rubidium 87 atoms are held in a magnetic surface trap allowing strong transverse confinement. The variety of phases in this reduced dimension is very rich, from the weakly interacting quasi-condensates to the fermionised regimes and strongly correlated phases, and the abundant theoretical tools allow quantitative comparison between theory and experiment. Moreoever the uniform 1D Bose gas has an integrable hamiltonian making this system an ideal test bench for studying out of equilibrium dynamics in the very active context of relaxation of isolated quantum many-body systems. |
Toolbox
|
|
|
Recent results:
- Probing the local rapidity distribution of one-dimensionnal gases
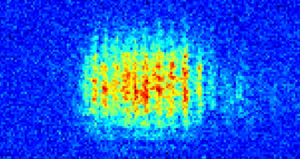
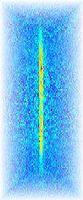
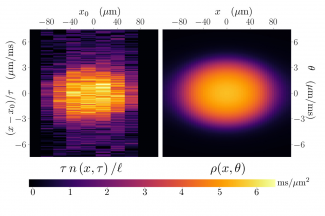
The cold atom gases realised in our experiment are well modeled by the Lieb-Liniger model which describes 1D Bosons with contact interactions. This paradigmatic model of N-body physics belongs to the class of integrable models. This property implies that the system supports quasi-particles of infinite lifetime, labeled by their velocity $\theta$ called rapidity. The rapidity distribution per unit length $\rho(\theta)$ plays a key role in the description of 1D gases. The rapidity distribution of a system is measurable: upon 1D expansion on very large sizes, while the rapidity distribution is conserved, the quasi-particles transform into "true" particles such that the velocity distribution of the atoms converges towards the rapidity distribution. The density distribution of the atoms also becomes homothetic to the rapidity distribution.
For non-homogeneous gases that vary on long wavelengths, one can defined the local rapidity distribution $\rho(x,\theta)$. To measure the local rapidity distribution, we first select a small slice of the gas around $x$ using a pushing beam shaped spatially with the DMD, and then we measure its rapidity distribution by letting the slice expand in 1D. We demonstrate the implementation of this technics to a cloud at equilibrium in a longitudinal potential and we also apply it to unveil out-of-equilibrium dynamics.
For more information : PhysRevLett, 133, 113402 (2024)
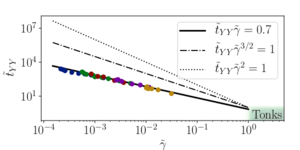
- First demonstration of the validity of the Generalised Hydrodynamics
Discribing the out-of-equilibrium dynamics of many-body quantum systems is a priori a tremendously difficult task. However, a recent theoretical development provides an ab-initio description of the long wavelength dynamics of 1D integrable quantum systems, the so-called Generalised Hydrodynamics (GHD). In contrast to conventional hydrodynamics, GHD does not assume that gas is locally described by the Gibbs ensemble but it keeps track of all conserved quantities of the integrable system. In cold atom experiments, 1D bosonic gases are realised, which are well described by the famous integrable Lieb-Liniger model. Cold atom experiments thus offer an ideal platform to test GHD.
We use our atom-chip experiment to test experimentally GHD. Starting from a cold atomic cloud at thermal equilibrium, dynamics is generated by a sudden quench of the longitudinal potential. The measured time evolution of the density profiles are in excellent agreement with predictions from GHD. We also compare our data with predictions from the conventional hydrodynamics method, which assumes locally a thermal equilibrium described by a Gibbs ensemble. Except for the special case of harmonic potentials, we find that conventional hydrodynamics completely fails to reproduce our data. Hydrodynamics even predicts the development of sharp structures leading to a chock phenomena, such a phenomena being absent in the data and in the GHD description.
For more information : Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 090601 (2019) : "Generalized Hydrodynamics on an Atom Chip", M. Schemmer, I. Bouchoule, B. Doyon, and J. Dubail
- Cooling a Bose gas by 3-body losses
Cold atomic cloud are metastable states, the ground state being a solid, and the cold clouds are plagged with 3-body process were a depply bound molecule is formed in the course of a 3-body collision. The binding energy is released in the form of kinetic energy of the molecule and the remaining atom, typically much larger than the trap depth and the 3-body process thus amount to the loss of 3 atoms : each recombination event results in the loss of 3 atoms. As a dissipative process, the 3-body losses are usually considered as detrimental for cold gases. Since they occur predominantly in the regions of small trapping energy, where the atomic density is the largest, they are known to heat a thermal gases by an anti-evaporation process. In our experiment, we demonstrate experimentally for the first time cooling due to 3-body losses. More precisely, we use a harmonically confined one-dimensional Bose gas in the quasi-condensate regime and use density ripples analysis to extract the temperature of the phonon modes. As the atom number decreases under the effect of three-body losses, the temperature drops up to a factor four. The ratio $k_B T /mc^2$ stays close to 0.64, where $c$ is the speed of sound in the trap center and $m$ the atomic mass. This value is close to the stationnary value predicted by the theory. In terms of the 1D dimensionless parameter $\gamma$ characterizing the strength of the interactions, our different data sets span more than two orders of magnitude.
Pour plus de détails : "Cooling a Bose Gas by Three-Body Losses".Physical Review Letters, 121 , pp.200401 (2018)
- Monitoring squeezed collective modes of a 1D Bose gas after an interaction quench
The effective 1D interaction strength depends on the tranverse confinement of the atoms.Thanks to the versatility of our modulated guide, we can change the transverse confinement, independantly on the longitudinal one. We can thus realise quenches of the interaction strength of the 1D gas and we investigated the out-of-equilibrium dynamics following a sudden quench of the interaction strength. Within a linearized approximation, the system is described by independent collective modes (the Bogoliubov modes, or equivalently the modes of the Luttinger-Liquid model) and the quench squeezes the phase space distribution of each mode, leading to a subsequent breathing of each quadrature.
We show that the collective modes are resolved by the power spectrum of density ripples which appear after a short time of flight. This allows us to experimentally probe the expected breathing phenomenon. Our results are in good agreement with theoretical predictions which take the longitudinal harmonic confinement into account.For more information, see Physical Review A, 98, p.043604 (2018)
- Dissipative cooling of a quasi-condensate : theoretical investigation
Ultra-cold temperatures are routinely obtained in cold atoms experiments using evaporative cooling. An energy-selective loss process removes the most energetic atoms; provided these atoms have a high enough energy, rethermalization of the remaining atoms leads to a lower temperature. Evaporative cooling however becomes unefficient once the transverse degrees of freedom are frozen. Cooling then relies on a simple one-body loss process, as shown in the group of J. Schmiedmayer in Vienna (Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 030402 (2016), Phys. Rev. A 93, 033634 (2016)). We showed that this cooling produces non thermal states, whose long-lived nature is garantied by the integrability of the model of bosonic atoms with contact interactions. We also developp a Monte-Camro wave function analysis of this cooling mecanism, which enable us to propose a quantum feedback scheme to cool to ground state one or several collective modes. Finally, we substantially extended previous work by investigating the effect of j-body losses, i.e. losses due to collosionnal process involving j atoms and where j atoms are lost at each event.
Cooling due to losses is seen on low energy collective modes, the phonon modes. The temperature of those modes results from a competition between two effetcs. On the one hand losses produce a reduction of the energy in each phonon mode since a smaller amplitude of density modulations lowers the interaction energy of each phonon mode. On the other hand, the shot noise due to the discrete nature of losses is responsible for an increase of the density fluctuations in the gas, and thus increases the energy in each mode. The competition between these two processes leads to a decay of the temperature such that the ratio between $k_B T$ and $mc^2$, where $m$ is the atomic mass and $c$ the speed of sound, becomes asymptotically a constant, of the order of unity.
For more detail see our publications :"Cooling phonon modes of a Bose condensate with uniform few body losses". SciPost Physics, vol.5 , p.043 (2018); "Long-lived non-thermal states realized by atom losses in one-dimensional quasi-condensates", Physical Review A 96, pp.013623 (2017); "A Monte Carlo wavefunction description of losses in a 1D Bose gas and cooling to the ground state by quantum feedback." Physical Review A 95, pp.043641 (2017)
- Momentum-Space Correlations of a One-Dimensional Bose Gas
Analyzing the noise in the momentum profiles of single realizations of one-dimensional Bose gases, we present the experimental measurement of the full momentum-space density correlations, which are related to the two-body momentum correlation function. Our data span the weakly interacting region of the phase diagram, going from the ideal Bose gas regime to the quasicondensate regime. We show experimentally that the bunching phenomenon, which manifests itself as super-Poissonian local fluctuations in momentum space, is present in all regimes. The quasicondensate regime is, however, characterized by the presence of negative correlations between different momenta, in contrast to the Bogolyubov theory for Bose condensates, predicting positive correlations between opposite momenta. Our data are in good agreement with ab initio calculations : either simplified models valid ion the asymptotic regimes of Ideal Bose gas and quasi-condensates respectively, or quantum Monte Carlo calculations performed by Tommaso Roscilde.
- Self-reflexion mecanism in the breathing of a 1D quasicondensate
We investigated the breathing mode of quasi-condensates both in real space and in momentum space. The profile in real space reveals sinusoidal width oscillations whose frequency varies continuously through the quasicondensate to ideal Bose gas crossover. In momentum space and for cold enough quasi-condensates, we report the first observation of a frequency doubling phenomenon : the width of the momentum distribution shows two minima per breathing period, at the outer turning point when the real-space density distribution is the largest and at the inner turning point when the cloud is the thinnest. The narrowing of the momentum width at the inner turning point corresponds to a self-reflection mechanism due to the repulsive interactions. The disappearance of the frequency doubling as the temperature of the gaz is increased is mapped out experimentally.
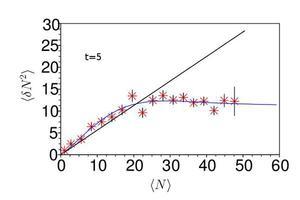
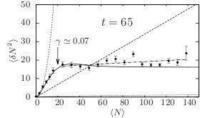
- Sub-poissonian density fluctuations in a repulsive 1D Bose gas
In situ density fluctuation measurements were used to probe the different regimes of a repulsive 1D Bose gas. The repulsive interactions suppress bosonic bunching in the quasi-condensate phase leading to a reduction of the density fluctuations. We mapped the phase diagram by tuning temperature and interaction strength. Density fluctuation measurements can also be used as a thermometry.
For weakly interacting gases (right), we observed fluctuations that are super-poissonian (due to bosonic bunching) at intermediate densities and which become sub-poissonian at large density, in the quantum quasi-condensate regime. At larger interaction strengths (left), the gas is close to the fermionised regime. Here the fluctuations are close to poissonian, a feature that resembles what is expected for a Fermi gas.
For more information, see "Sub-Poissonian Fluctuations in a 1D Bose Gas: From the Quantum Quasicondensate to the Strongly Interacting Regime Thibaut Jacqmin, Julien Armijo, Tarik Berrada, Karen V. Kheruntsyan, and Isabelle Bouchoule, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 230405
Ongoing work:
- Studying out-of-equlibrium dynamics using the local rapidity distribution probe
- Implementing an optical longitudianl trapping
Internship proposal:
M2 internship proposal: Effect of controlled losses on a one-dimensional bose gas
List of publications
- Probing the Local Rapidity Distribution of a One-Dimensional Bose Gas: L. Dubois, G. Thémèze, F. Nogrette, J. Dubail, and I. Bouchoule, Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 113402 – Published 12 September 2024
- Generalized HydroDynamics on an Atom Chip : Max Schemmer, Isabelle Bouchoule, Benjamin Doyon, Jerome Dubail, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 090601 (2019)
- Cooling a Bose Gas by Three-Body Losses. : Max Schemmer, Isabelle Bouchoule, Physical Review Letters, 2018, vol.121 (20), pp.200401.
- Monitoring squeezed collective modes of a one-dimensional Bose gas after an interaction quench using density ripples analysis. : Max Schemmer, Aisling Johnson, Isabelle Bouchoule. Physical Review A, 2018, vol. 98, pp.043604.
- Cooling phonon modes of a Bose condensate with uniform few body losses : Isabelle Bouchoule, Max Schemmer, Carsten Henkel. SciPost Physics, 2018, 5 (5)
- Long-Lived nonthermal states realized by atom losses in one-dimensional quasicondensates. Aisling Johnson, Stuart S. Szigeti, Maximilian Schemmer and Isabelle Bouchoule, Phys. Rev. A 96, 013623 (2017)
- Monte CArlo wave-function description of losses in a one-dimensionnal Bose gas and cooling to the ground state by quantum feedback. Maximilian Schemmer, Aisling Johnson, R. Photopoulos and I. Bouchoule, Phys. Rev. A 95, 043641 (2017)
- Momentum Space Correlations of a One-Dimensional Bose Gas.
Bess Fang, Aisling Johnson, Tommaso Roscilde, and Isabelle Bouchoule, Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 050402 - Quench-Induced Breathing Mode of One-Dimensional Bose Gases
Bess Fang, Giuseppe Carleo, Aisling Johnson, and Isabelle Bouchoule, Physical Review Letters 113 (2014) 053301 - Momentum distribution of one-dimensional Bose gases at the quasicondensation crossover: Theoretical and experimental investigation
Thibaut Jacqmin, Bess Fang, Tarik Berrada, Tommaso Roscilde, and Isabelle Bouchoule, Physical Review A 86 (2012) 043626 - Two-body momentum correlations in a weakly-interacting one-dimensional Bose gas
Bouchoule I, Arzamazovs M, Kheruntsyan K.V., Gangardt D.M.
Physical Review A: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics (2012) vol. 86, p. 033626 - Sub-Poissonian fluctuations in a 1D Bose gas: from the quantum quasi-condensate to the strongly interacting regime
Jacqmin T., Armijo J., Berrada T., Kheruntsyan K., Bouchoule I.
Physical Review Letters 106 (2011) 230405 - Mapping out the quasi-condensate transition through the 1D-3D dimensional crossover
Armijo J., Jacqmin T., Kheruntsyan K., Bouchoule I.
Physical Review A: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics (2011) vol. 83, p. 021605 - Probing three-body correlations in a quantum gas using the measurement of the third moment of density fluctuations
Armijo J., Jacqmin T., Kheruntsyan K., Bouchoule I.Physical Review Letters 105 (2010) 230402 - Thermal properties of AlN-based atom chips Armijo J., Garrido Alzar C., Bouchoule I. European Physical Journal D 56 (2009
- Limitation of the modulation method to smooth wire guide roughness Bouchoule I., Trebbia J.-B., Garrido Alzar C. Physical Review A: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 77 (2008) 023624
- Roughness suppression via rapid current modulation on an atom chip Trebbia J.-B., Garrido Alzar C., Cornelussen R., Westbrook C. I., Bouchoule I. Physical Review Letters 98, 263201 (2007)
- Observations of density fluctuations in an elongated Bose gas: ideal gas and quasi-condensate regimes Estève J., Trebbia J.-B., Schumm T., Aspect A., Westbrook C. I., Bouchoule I. Physical Review Letters 96 (2006) 130403
- Experimental evidence for the breakdown of a Hartree-Fock approach in a weakly interacting Bose gas Trebbia J.-B., Estève J., Westbrook C. I., Bouchoule I. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 (2006)
- Realizing a stable magnetic double-well potential on an atom chip Estève J., Schumm T., Trebbia J.-B., Bouchoule I., Aspect A., Westbrook C. I. European Physical Journal D 35 (2005)
- Atom chips in the real world: the effects of wire corrugation Schumm T., Estève J., Aussibal C., Figl C., Trebbia J.-B., Nguyen H., Mailly D., Bouchoule I., Westbrook C. I., Aspect A. European Physical Journal D 32 (2005)
- The role of wire imperfections in micro magnetic traps for atoms Estève J., Aussibal C., Schumm T., Figl C., Mailly D., Bouchoule I., Westbrook C. I., Aspect A. Physical Review A: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 70 (2004)